|
Background
Italy, officially the Italian Republic (Italian: Repubblica Italiana), is a country located on the Italian Peninsula in Southern Europe and on the two largest islands in the Mediterranean Sea, Sicily and Sardinia. Italy shares its northern, Alpine boundary with France, Switzerland, Austria and Slovenia. The independent states of San Marino and the Vatican City are enclaves within the Italian Peninsula, and Campione d'Italia is an Italian exclave in Switzerland.
Italy has been the home of many European cultures, such as the Etruscans and the Romans, and later was the birthplace of the university and of the Renaissance, that began in Tuscany and spread all over Europe. Italy's capital, Rome, was for centuries the center of Western civilization. Italy possessed a colonial empire from the second half of the nineteenth century to the mid-twentieth century.
Today, Italy is a democratic republic and a developed country with the eighth-highest quality-of-life index rating in the world.[4] It is a founding member of what is now the European Union, having signed the Treaty of Rome in 1957, and it is a founding member of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). It is a member of the G8, having the world's seventh-largest nominal GDP, and is also a member state of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), the World Trade Organization (WTO), the Council of Europe, the Western European Union, and the Central European Initiative. Italy is a Schengen state. It has the world's seventh-largest defence budget and shares NATO's nuclear weapons. On 1 January 2007, Italy began a two-year term as a non-permanent member of the United Nations Security Council.
Politics
The politics of Italy take place in a framework of a parliamentary, democratic republic, and of a multi-party system.
The President of the Italian Republic (Presidente della Repubblica) is elected for seven years by the parliament sitting jointly with a small number of regional delegates. As the head of state, the President of the Republic represents the unity of the nation and has many of the duties previously given to the King of Italy. The president serves as a point of connection between the three branches of power: he is elected by the lawmakers, he appoints the executive, he is the president of the judiciary and he is also the commander-in-chief of the armed forces. The president nominates the Prime Minister, who proposes the other ministers (formally named by the president). The Council of Ministers must obtain a confidence vote from both houses of Parliament. Legislative bills may originate in either house and must be passed by a majority in both.
A peculiarity of the Italian Parliament is the representation given to Italian citizens permanently living abroad (about 2.7 million people). Among the 630 Deputies and the 315 Senators there are respectively 12 and 6 elected in four distinct overseas constituencies. Those members of Parliament were elected for the first time in April 2006, and they have the same rights as members elected in Italy.
The Italian judicial system is based on Roman law modified by the Napoleonic code and later statutes. The Supreme Court of Cassation is the court of last resort for most disputes. The Constitutional Court of Italy (Corte Costituzionale) rules on the conformity of laws with the Constitution and is a post-World War II innovation.
Administrative divisions
Italy is subdivided into 20 regions (regioni, singular regione). Five of these regions have a special autonomous status that enables them to enact legislation on some of their local matters; these are marked by an asterisk (*) in the table below. The country is further divided into 109 provinces (province) and 8,101 municipalities (comuni).
|
Region |
Capital |
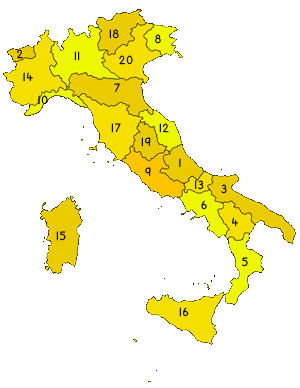 |
| 1. Abruzzo |
L'Aquila |
| 2. Aosta Valley* |
Aosta |
| 3. Apulia |
Bari |
| 4. Basilicata |
Potenza |
| 5. Calabria |
Catanzaro |
| 6. Campania |
Naples |
| 7. Emilia-Romagna |
Bologna |
| 8. Friuli-Venezia Giulia* |
Trieste |
| 9. Lazio |
Rome |
| 10. Liguria |
Genoa |
| 11. Lombardy |
Milan |
| 12. Marche |
Ancona |
| 13. Molise |
Campbasso |
| 14. Piedmont |
Turin |
| 15. Sardinia* |
Cagliari |
| 16. Sicily* |
Palermo |
| 17. Tuscany |
Florence |
| 18. Trentino- Alto Adige* |
Trento |
| 19. Umbria |
Perugia |
| 20. Veneto |
Venice |
Economic overview
According to GDP calculations, Italy was ranked as the seventh-largest economy in the world in 2006, behind the United States, Japan, Germany, China, the United Kingdom, and France, and the fourth-largest in Europe. According to the OECD, in 2004 Italy was the world's sixth-largest exporter of manufactured goods. This economy remains divided into a developed industrial north dominated by private companies and a less-developed agricultural south. In the Index of Economic Freedom 2008 it ranked 64th of 162 countries, or 29th of 41 European countries, the lowest rating in the EU-15 and behind many ex-communist European countries. Italy has often been called a sick man of Europe, with governments having problems in pursuing reform programs.
According to World Bank data, Italy has high levels of freedom to invest, do business, and trade. On the other hand, compared to other European countries, Italy has inefficient bureaucracy, relatively low property rights, heavy taxes, and heavy public consumption at around half of GDP. Italy has been in economic decline compared to most other EU-15 countries. Most raw materials needed by Italian industries, and more than 75% of energy requirements, are imported. Over the past decade, Italy has pursued a tight fiscal policy in order to meet the requirements of the Economic and Monetary Union and has benefited from lower interest and inflation rates. Italy joined the euro from its introduction in 1999.
Italy is a member state of the European Union and part of its single market.Italy has a smaller number of world-class multinational corporations than other economies of comparable size. Instead, the country's main economic strength has been its large base of small- and medium-sized companies. Some of these companies manufacture products that are technologically moderately advanced and therefore face increasing competition from China and other emerging Asian economies which are able to undercut them on labour costs. These Italian companies are responding to the Asian competition by concentrating on products with a higher technological content, while moving lower-tech manufacturing to plants in countries where labour is less expensive. The small average size of Italian companies remains a limiting factor, and the government has been working to encourage integration and mergers and to reform the rigid regulations that have traditionally been an obstacle to the development of larger corporations in the country. Nevertheless, Italian industry is envied for its advanced design and style, which often capitalize on the country's formidable artistic patrimony.
Italy's major exports are motor vehicles (Fiat Group, Aprilia, Ducati, Piaggio), chemicals, petrochemicals (Eni), electricity (Enel, Edison), home appliances (Merloni, Candy), aerospace and defense tech (Alenia, Agusta, Finmeccanica), and firearms (Beretta), but the country's more famous exports are in the fields of fashion (Armani, Valentino, Versace, Dolce & Gabbana, Roberto Cavalli, Benetton, Prada, Luxottica), food industry (Ferrero, Barilla Group, Martini & Rossi, Campari, Parmalat), luxury vehicles (Ferrari, Maserati, Lamborghini, Pagani) and motoryachts (Ferretti, Azimut).
Also tourism is very important to the Italian economy: with over 43.7 million tourists a year, Italy is ranked as the fifth major tourist destination in the world.
Foreign Relations Italy was a founding member of the European Community—now the European Union (EU). Italy was admitted to the United Nations in 1955 and is a member and strong supporter of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade/World Trade Organization (GATT/WTO), the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), and the Council of Europe. Its recent turns in the rotating Presidency of international organisations include the Conference for Security and Co-operation in Europe (CSCE), the forerunner of the OSCE, in 1994; G8; and the EU in 2001 and from July to December 2003.
Italy supports the United Nations and its international security activities. Italy deployed troops in support of UN peacekeeping missions in Somalia, Mozambique, and East Timor and provides support for NATO and UN operations in Bosnia, Kosovo and Albania. Italy deployed over 2,000 troops to Afghanistan in support of Operation Enduring Freedom (OEF) in February 2003. Italy still supports international efforts to reconstruct and stabilize Iraq, but it has withdrawn its military contingent of some 3,200 troops as of November 2006, maintaining only humanitarian workers and other civilian personnel. In August 2006 Italy sent about 2,450 soldiers to Lebanon for the United Nations' peacekeeping mission UNIFIL.
Infrastructure
The railway network in Italy, operated by Ferrovie dello Stato, totals 16,627 kilometres (10,331 mi), ranking the country 17th in the world. High-speed trains include ETR-class trains, of which the ETR 500 travels at 300 km/h (190 mph). The version ETR 500 Y1 achieved 355 km/h (221 mph) on the Milan-Bologna line on 1 March 2008.
There are approximately 654,676 km (406,797 mi) of serviceable roadway in Italy, including 6,957 km (4,323 mi) of expressways. There are approximately 133 airports in Italy, including the two hubs of Malpensa International near Milan and Leonardo Da Vinci International near Rome. There are 27 major ports in Italy, the largest in Genoa, which is also the second-largest in the Mediterranean Sea after Marseille. Italy is traversed by 2,400 km (1,500 mi) of waterways.
|