|
Background
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is the second largest country in South America, constituted as a federation of 23 provinces and an autonomous city, Buenos Aires. It is the eighth largest country in the world by land area and the largest among Spanish-speaking nations, though Mexico, Colombia and Spain are more populous.
Argentina's continental area is between the Andes mountain range in the west and the Atlantic Ocean in the east. It borders Paraguay and Bolivia to the north, Brazil and Uruguay to the northeast, and Chile to the west and south.
Argentina has the second-highest Human Development Index and GDP per capita in purchasing power parity in Latin America. Argentina is one of the G-20 major economies, with the world's 30th largest nominal GDP, and the 23rd largest when purchasing power is taken into account. The country is classified as upper-middle income or a secondary emerging market by the World Bank.
Politics
The Argentine Constitution of 1853 mandates a separation of powers into executive, legislative, and judicial branches at the national and provincial level. The political framework is a federal representative democratic republic, in which the President is both head of state and head of government, complemented by a pluriform multi-party system.
Executive power resides in the President and the Cabinet. The President and Vice President are directly elected to four-year terms and are limited to two terms. Cabinet ministers are appointed by the President and are not subject to legislative ratification. The current President is Cristina Fernández de Kirchner, with Julio Cobos as Vice President.
Legislative power is vested in the bicameral National Congress, comprising a 72-member Senate and a 257-member Chamber of Deputies. Senators serve six-year terms, with one-third standing for re-election every two years. Members of the Chamber of Deputies are elected to four-year terms by a proportional representation system, with half of the members standing for re-election every two years. A third of the candidates presented by the parties must be women.
Administrative divisions
Argentina is divided into twenty-three provinces (provincias; singular provincia) and one autonomous city. Buenos Aires province is divided into 134 partidos, while the remaining provinces are divided into 376 departments (departamentos). Departments and partidos are further subdivided into municipalities or districts.
|
Province |
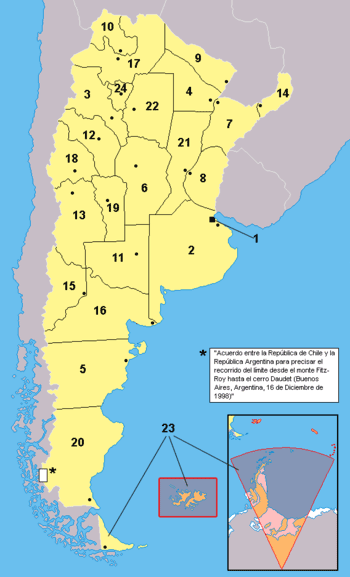 |
| 1. City of Buenos Aires |
| 2. Buenos Aires Province |
| 3. Catamarca Province |
| 4. Chaco Province |
| 5. Chubut Province |
| 6. Córdoba Province |
| 7. Corrientes Province |
| 8. Entre Ríos Province |
| 9. Formosa Province |
| 10. Jujuy Province |
| 11. La Pampa Province |
| 12. La Rioja Province |
| 13. Mendoza Province |
| 14. Misiones Province |
| 15. Neuquén Province |
| 16. Río Negro Province |
| 17. Salta Province |
| 18. San Juan Province |
| 19. San Luis Province |
| 20. Santa Cruz Province |
| 21. Santa Fe Province |
| 22. Santiago del Estero Province |
23. Tierra del Fuego
and disputed areas of Antarctica and the South Atlantic |
| 24. Tucumán Province |
Economic overview
Argentina has abundant natural resources, a well-educated population, an export-oriented agricultural sector and a relatively diversified industrial base. Domestic instability and global trends, however, contributed to Argentina's decline from its noteworthy position as the world's 10th wealthiest nation per capita in 1913 to that of an upper-middle income economy. Though no consensus exists explaining this, systemic problems have included increasingly burdensome debt, uncertainty over the monetary system, excessive regulation, barriers to free trade, and a weak rule of law coupled with corruption and a bloated bureaucracy. Even during its era of decline between 1930 and 1980, however, the Argentine economy created Latin America's largest proportional middle class; but this segment of the population has suffered from a series of economic crises between 1981 and 2002, when the relative decline became absolute.
Record foreign debt interest payments, tax evasion and capital flight resulted in a balance of payments crisis that plagued Argentina with serious stagflation from 1975 to 1990. Attempting to remedy this, economist Domingo Cavallo pegged the peso to the U.S. dollar in 1991 and limited the growth in the money supply. His team then embarked on a path of trade liberalization, deregulation and privatization. Inflation dropped and GDP grew by one third in four years; but external economic shocks and failures of the system diluted benefits, causing the economy to crumble slowly from 1995 until the collapse in 2001. That year and the next, the economy suffered its sharpest decline since 1930; by 2002, Argentina had defaulted on its debt, its GDP had shrunk, unemployment reached 25% and the peso had depreciated 70% after being devalued and floated.
In 2003 expansionary policies and commodity exports triggered a rebound in GDP. This trend has been largely maintained, creating millions of jobs and encouraging internal consumption. The socio-economic situation has been steadily improving and the economy grew around 9% annually for five consecutive years between 2003 and 2007 and 7% in 2008. Inflation, however, though officially hovering around 9% since 2006, has been privately estimated at over 15%, becoming a contentious issue again. The urban income poverty rate has dropped to 18% as of mid-2008, a third of the peak level observed in 2002, though still above the level prior to 1976. Income distribution, having improved since 2002, is still considerably unequal.
Foreign Policy
Argentina is a full member of the Mercosur block together with Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay and Venezuela; and five associate members: Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador and Peru. From 2006 Argentina has emphasised Mercosur, which has some supranational legislative functions, as its first international priority; by contrast, during the 1990s, it relied more heavily on its relationship with the United States. Argentina is a founding signatory and permanent consulting member of the Antarctic Treaty System and the Antarctic Treaty Secretariat is based in Buenos Aires.
Infrastructure
Argentina's transport infrastructure is relatively advanced. There are over 230,000 km (144,000 mi) of roads (not including private rural roads) of which 72,000 km (45,000 mi) are paved and 1,575 km (980 mi) are expressways, many of which are privatized tollways. Having doubled in length in recent years, multilane expressways now connect several major cities with more under construction. Expressways are, however, currently inadequate to deal with local traffic, as 9.2 million motor vehicles are registered nationally as of 2008 (230 per 1000 population).
The railway network has a total length of 34,059 km (21,170 mi).
Argentina has around 11,000 km (6,835 mi) of navigable waterways, and these carry more cargo than do the country's freight railways. This includes an extensive network of canals, though Argentina is blessed with ample natural waterways, as well; the most significant among these being the Río de la Plata, Paraná, Uruguay, Río Negro and Paraguay rivers.
|